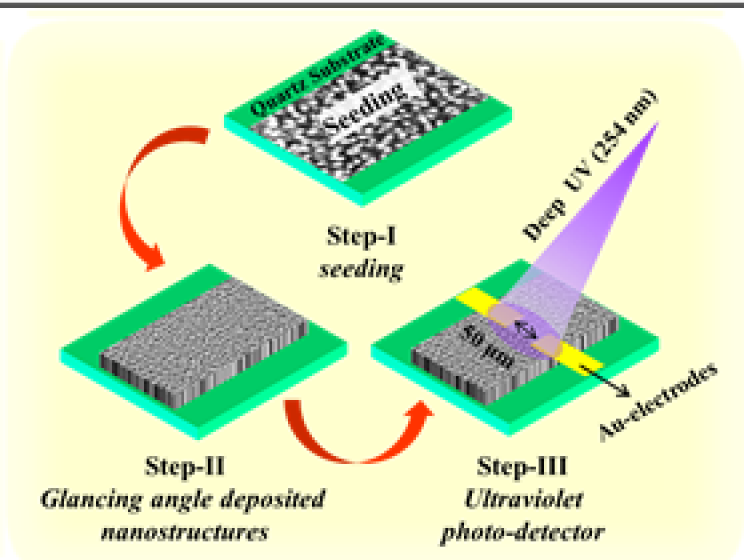
Figure 1: fabrication steps of ZnO nanostructures and ultraviolet photodetector (left) and time-dependent photo response of ZnO and Ga-doped ZnO UV photo detectors (right).
- Glancing angle deposition technique in combination with pulsed laser deposition (PLD) system has been used to prepare nanostructures of ZnO in Prof. Krushna R Mavani’s laboratory.
- This technique enables to produce of different shape, size, and a variety of morphology of the nanostructures by controlling the PLD parameters.
- The nanostructures acquire the wurtzite structure of ZnO and oriented along the c-axis.
- The ZnO nanostructures are deposited on amorphous (quartz) and crystalline substrates (sapphire and MgO).
- The prepared nanostructures are porous, defect-free and crystallographically oriented even on the quartz substrates.
- The nanostructures are grown in the vertical direction which increases the surface to volume ratio and also helps for ultraviolet (UV) light penetration at deep.
- The fabricated photodetectors are visible-blind and highly sensitive for UV light.
- The detectors are also applicable at low temperatures and at diverse environmental conditions, ensuring the applicability of the detectors for space-related applications.
Reference: “UV activated visible-blind ultraviolet Ga:ZnO photodetectors using the GLAD technique: a comparative study under different gas atmospheres and temperatures”
Ankit Soni, Komal Mulchandani, K. R. Mavani
J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8, 7837-7846. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TC00990C. (Impact factor: 7.059)